ความโน้มถ่วง
จากวิกิพีเดีย สารานุกรมเสรี
ความโน้มถ่วง (อังกฤษ: gravity) หรือ แรงโน้มถ่วง (อังกฤษ: gravitational force) ในทางฟิสิกส์ คือแรงที่กระทำระหว่างมวล แรงโน้มถ่วงเป็นหนึ่งในสี่แรงหลัก ซึ่งประกอบด้วย แรงโน้มถ่วง แรงแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้า แรงนิวเคลียร์แบบอ่อน และ แรงนิวเคลียร์แบบเข้ม ในจำนวนแรงทั้งสี่แรงหลัก แรงโน้มถ่วงมีค่าน้อยที่สุด ถึงแม้ว่าแรงโน้มถ่วงจะเป็นแรงที่เราไม่สามารถรับรู้ได้มากนักเพราะความเบาบางของแรงที่กระทำต่อเรา แต่ก็เป็นแรงเดียวที่ยึดเหนี่ยวเราไว้กับพื้นโลก แรงโน้มถ่วงมีความแรงแปรผันตรงกับมวล และแปรผกผันกับระยะทางยกกำลังสอง ไม่มีการลดทอนหรือถูกดูดซับเนื่องจากมวลใดๆ ทำให้แรงโน้มถ่วงเป็นแรงที่สำคัญมากในการยึดเหนี่ยวเอกภพไว้ด้วยกัน
นอกเหนือจากความโน้มถ่วงที่เกิดระหว่างมวลแล้ว ความโน้มถ่วงยังสามารถเกิดขึ้นได้จากการที่เราเปลี่ยนสภาพการเคลื่อนที่ตามกฎการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน เช่น การเพิ่มหรือลดความเร็วของวัตถุ การเปลี่ยนทิศทางการเคลื่อนที่ เป็นต้น
Gravitation (English: gravity) or gravity (English: gravitational force) in physics is the force acting between the masses. Gravity is one of the main force. Which include gravity, the electromagnetic force. Weak force and the strong force. All four of the main force. Gravity is minimal. Although gravity is a force that we can not know too much about it because the light of the forces acting on us. However, it is the only thing holding me to the ground. Gravity is a force proportional to their mass. And inversely proportional to the distance squared. No attenuation or absorption of any mass. Gravity is the force that makes it very important to hold the universe together. In addition to the gravity of the mass. Gravity can also arise from the fact that we changed to follow Newton's laws of motion, such as increasing or decreasing the speed of the object. To change the direction of travel, etc.
แรงโน้มถ่วง
การปฏิวัติทางวิทยาศาสตร์
หม่ในทฤษฎีแรงโน้มถ่วงเริ่มต้นด้วยการทำงานของกาลิเลโอ กาลิเลอีในปลายศตวรรษที่ 16 และต้นศตวรรษที่ 17 ในการทดลองที่โด่งดังของเขา (แม้ว่าหลักฐานที่อ้างอิงเกี่ยวกับเรื่องนี้อาจจะเป็นคัมภีร์นอกสารบบ) คือการทดลองปล่อยลูกบอลจากหอเอนเมืองปิซา,
The Scientific Revolution
In the gravity theory began with the work of Galileo. Galilei in the late 16th century and early 17th century in his famous experiments. (Although the evidence that this may be a reference to the Biblical Scholar) is an experimental release the ball from the Leaning Tower of Pisa.
กฎความโน้มถ่วงของนิวตัน Newton's law of gravitation
ในปี พ.ศ. 2230 ไอแซก นิวตัน ได้ค้นพบกฎความโน้มถ่วงดังนี้
- {|
| F || แทนความโน้มถ่วงระหว่างมวลทั้งสอง |- | G || แทนค่านิจโน้มถ่วงสากล |- | m1 || แทนมวลของวัตถุแรก |- | m2 || แทนมวลของวัตถุที่สอง |- | r || แทนระยะห่างระหว่างวัตถุทั้งสอง |}
นั่นคือความโน้มถ่วงแปรผันตรงกับมวล (มวลมากก็มีความโน้มถ่วงมาก) และแปรผกผันกับระยะห่างกำลังสอง (ระยะห่างมากก็มีความโน้มถ่วงน้อย)
ทฤษฎีสัมพัทธภาพทั่วไป
Albert Einstein ได้เผยแพร่ทฤษฎีสัมพัทธภาพทั่วไปในปี พ.ศ. 2459 โดยเนื้อหาแสดงถึงการอธิบายความโน้มถ่วงที่มีพื้นฐานมาจากทฤษฎีสัมพัทธภาพพิเศษและกฎความโน้มถ่วงของนิวตันในรูปแบบของกาลอวกาศ (อังกฤษ: Spacetime) เชิงเรขาคณิตที่สามารถอธิบายได้ด้วยสมการสนามของAlbert Einstein (อังกฤษ: Einstein field Equation) ดังนี้
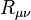 | แทน ริชชี่เทนเซอร์ความโค้ง (Ricci Tensor Curvature) |
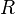 | แทนความโค้งเชิงสเกลาร์ (Scalar Curvature) |
 | แทนเมตริกซ์เทนเซอร์ |
 | แทนค่าคงตัวจักรวาล (Cosmological Constant) |
 | แทนค่านิจโน้มถ่วงสากล (Gravity Constant) |
 | แทนความเร็วแสง |
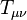 | แทนเทนเซอร์ความเค้น-พลังงาน (Stress-Energy Tensor) |
ความโน้มถ่วงของโลก
จากกฎความโน้มถ่วงของนิวตัน แรงโน้มถ่วงของโลกที่กระทำกับมวลใดๆ จะขึ้นอยู่กับระยะทางระหว่างศูนย์กลางมวลของโลกกับศูนย์กลางมวลวัตถุยกกำลังสอง ดังนั้นแรงโน้มถ่วงของโลกบริเวณต่างๆ จึงมีค่าไม่เท่ากัน และเนื่องจากโลกมีการหมุนรอบตัวเองมีผลทำให้เกิดแรงหนีศูนย์กลาง แรงหนีศูนย์กลางนี้จะหักล้างกับแรงโน้มถ่วงของโลก แรงหนีศูนย์กลางจะมีค่ามากที่สุดบริเวณเส้นศูนย์สูตร และมีค่าน้อยที่สุดบริเวณขั้วโลก ผลของแรงหนีศูนย์กลางนี้ทำให้แรงโน้มถ่วงของโลกบริเวณเส้นศูนย์สูตรมีค่าน้อยกว่าแรงโน้มถ่วงของโลกบริเวณขั้วโลกเหนือ นอกจากนั้น โลกก็มิได้เป็นทรงกลมโดยสมบูรณ์ แต่แป้นตรงกลางเล็กน้อยคล้ายผลส้ม ทำให้ระยะห่างจากจุดศูนย์กลางของโลกถึงพื้นผิวโลกแปรผันไปตามละติจูด
สำหรับการคำนวณทางวิศวกรรมโดยทั่วไปความเปลี่ยนแปลงของค่าแรงโน้มถ่วงไม่ถือเป็นนัยสำคัญ จึงสามารถใช้ค่าเฉลี่ยของแรงโน้มถ่วงของโลกได้ โดยกำหนดให้ ความเร่งเนื่องจากความโน้มถ่วงของโลก (g) มีค่าเท่ากับประมาณ 9.81(~10) เมตรต่อวินาทีกำลังสอง
Earth's gravitational From Newton's law of gravitation. The force of gravity acting on any mass. Is based on the distance between the centers of mass of the Earth and the center of mass squared. The gravity of the area. Are not the same And because the world is spinning around itself with resultant centrifugal force. Centrifugal forces are offset against the force of gravity. Equatorial centrifugal force will be most valuable. And the minimum polar regions. The effect of centrifugal force, the force of gravity, making the equatorial region is less than the force of gravity at the north pole in the world is not a perfect sphere by. The middle pedal slightly orange. The distance from the center of the earth to the earth's surface varies according to latitude.
For engineering calculations, in general, the dynamics of gravity is not considered significant. We can use the average of the force of gravity is determined by the Earth's gravitational acceleration (g) is equal to about 9.81 (~ 10) meters per second squared.


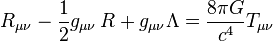
ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น